What is Vitamin K2 (Menaquinone)?

What is Vitamin K2? It’s a vital nutrient that plays a key role in maintaining strong bones and a healthy heart. Vitamin K2, also known as menaquinone, is one of the two main forms of vitamin K, the other being vitamin K1 (phylloquinone). Unlike vitamin K1, which is mainly involved in blood clotting, vitamin K2 plays a crucial role in bone health, calcium metabolism, and cardiovascular protection.
- What is Vitamin K2 (Menaquinone)?
- Health Benefits of Vitamin K2
- 1. Strengthens Bones and Prevents Osteoporosis
- 2. Supports Heart and Artery Health
- 3. Aids in Blood Clotting
- 4. Enhances Dental Health
- 5. Works Synergistically with Other Nutrients
- Food Sources of Vitamin K2
- Vitamin K2 Deficiency: Symptoms and Risks
- reatment of Vitamin K2 Deficiency
- 1. Dietary Changes
- 2. Supplements
- 3. Medical Treatment
- How Much Vitamin K2 Do You Need Daily?
Vitamin K2 is a fat-soluble vitamin, meaning it is absorbed with dietary fats and stored in the body’s fatty tissues. Although the human body can produce some vitamin K2 through gut bacteria, the amount is often insufficient. Therefore, obtaining vitamin K2 from food sources or supplements is essential to maintain optimal health.
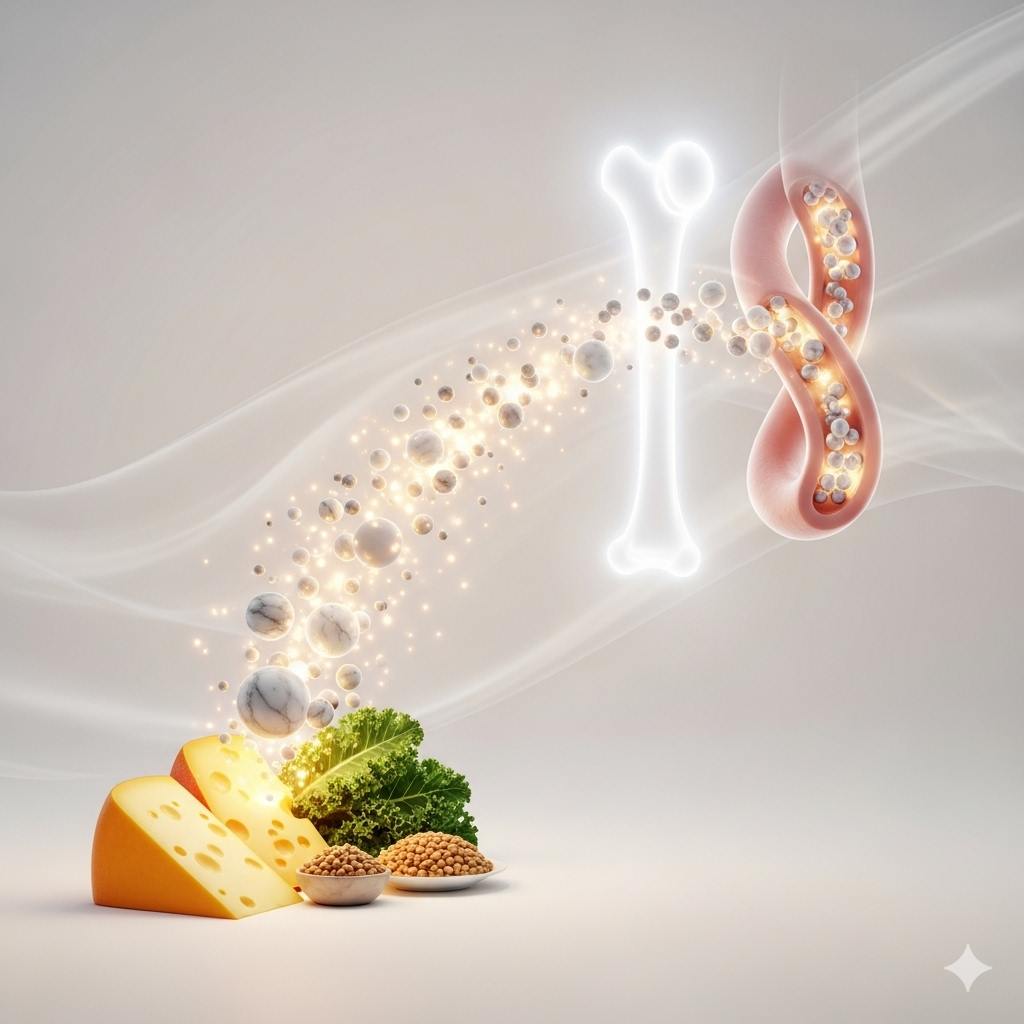
Research shows that vitamin K2 helps direct calcium into bones and teeth while preventing it from depositing in arteries and soft tissues. This dual function makes K2 vital for both skeletal strength and heart health.

Health Benefits of Vitamin K2
1. Strengthens Bones and Prevents Osteoporosis
One of the most well-known benefits of vitamin K2 is its role in bone mineralization. K2 activates proteins such as osteocalcin, which help bind calcium to the bone matrix. Without sufficient K2, calcium may not reach the bones effectively, increasing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures, especially in older adults.
2. Supports Heart and Artery Health
Vitamin K2 prevents calcium from accumulating in the blood vessels. Studies suggest that people with higher K2 intake have lower risks of arterial calcification, heart attacks, and strokes. By regulating calcium, K2 helps maintain flexible and healthy arteries.
3. Aids in Blood Clotting
Like vitamin K1, K2 also contributes to blood clotting. It activates clotting factors in the liver, reducing the risk of excessive bleeding.
4. Enhances Dental Health
Research indicates that vitamin K2 may benefit dental health by improving tooth mineralization. Since osteocalcin also plays a role in dentin formation, K2 intake could support stronger, healthier teeth.
5. Works Synergistically with Other Nutrients
Vitamin K2 works best in combination with vitamin D3 and magnesium. While vitamin D increases calcium absorption, K2 ensures that calcium is directed to the right places. Magnesium further enhances this process, making the trio essential for bone and cardiovascular health.
Food Sources of Vitamin K2
Although vitamin K1 is abundant in green leafy vegetables, vitamin K2 is found in animal-based and fermented foods. Including these foods in your diet can help maintain adequate K2 levels:
- Natto (a Japanese fermented soybean dish, one of the richest sources of K2)
- Liver (especially beef and chicken liver)
- Egg yolks
- Cheese (especially hard and aged varieties)
- Kefir and yogurt
- Butter from grass-fed cows
- Chicken and beef
- Fermented vegetables like sauerkraut
- Fish and seafood (e.g., salmon, mackerel, and shrimp)
Fruits and vegetables such as spinach, broccoli, asparagus, figs, strawberries, and kiwi also provide small amounts of vitamin K2, although their content is much lower compared to fermented and animal-based sources.
Vitamin K2 Deficiency: Symptoms and Risks
Vitamin K2 deficiency is relatively rare but can occur due to poor diet, digestive disorders, or long-term use of antibiotics that disrupt gut bacteria. Some groups at higher risk include newborns, elderly individuals, and people with fat malabsorption conditions.
Common signs and risks of deficiency include:
- Easy bruising and frequent nosebleeds
- Excessive bleeding from minor injuries
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual periods in women
- Bone weakness and increased risk of fractures
- Tooth decay and poor dental health
- Calcification of arteries, raising the risk of cardiovascular disease
- Blood in stool (sometimes seen in children with severe deficiency)
reatment of Vitamin K2 Deficiency
If a deficiency is detected through medical tests, treatment depends on the severity:
1. Dietary Changes
Mild deficiency can often be corrected by eating more K2-rich foods such as cheese, eggs, yogurt, natto, and fermented vegetables.
2. Supplements
For individuals with severe deficiency or specific health conditions, vitamin K2 supplements (commonly in the forms MK-4 and MK-7) may be prescribed. MK-7, found in fermented foods like natto, has a longer half-life in the body, making it highly effective.
3. Medical Treatment
In cases where K2 deficiency is linked to blood clotting disorders, fat malabsorption, or liver disease, doctors may administer K2 through oral tablets or injections. The dosage and duration are determined by a healthcare professional.
How Much Vitamin K2 Do You Need Daily?
There is no universally established recommended daily intake (RDI) for vitamin K2, but many experts suggest a range between 90–120 micrograms per day for adults. Individual needs may vary depending on diet, lifestyle, and health conditions.
For best results, it is recommended to:
- Pair K2 with vitamin D and magnesium for maximum effectiveness.
- Choose whole food sources when possible.
- Consult a doctor before starting supplements, especially if you are taking blood thinners like warfarin.
Vitamin K2, or menaquinone, is an essential but often overlooked nutrient that supports bone strength, heart health, blood clotting, and dental wellness. While the body produces small amounts of K2, relying solely on this natural synthesis is often not enough. Incorporating K2-rich foods and, if necessary, supplements can help maintain optimal health and prevent long-term complications such as osteoporosis and cardiovascular disease.
By combining vitamin K2 with other key nutrients like vitamin D and magnesium, you can significantly improve your overall well-being, skeletal system, and cardiovascular protection.